Digilent defines Analog Discovery 2 as “a USB oscilloscope, logic analyzer, and multi-function instrument that allows users to measure, visualize, generate, record, and control mixed-signal circuits of all kinds”. At the time of writing this article, the price of Analog Discovery 2 is $279.00, and they offer Academic discounts starts at 25%.
It is funny enough to say that: If you used to count the oscilloscopes, power supplies and other tools in your favorite electronics engineering Youtuber videos background without being able to buy at least one item of those, then you should complete reading this review. if you don’t, also please complete reading!

8 Years back, I saw one of the early David Jones’ VLogs under the title of “How To Set Up An Electronics Lab“, and it was really hard for me as a student to afford the right budget to set up a real Electronics Lab. For example, Getting an affordable and entry-level Rigol oscilloscope (and only scope) was about $400 at that time. Even these days, getting an entry-level scope costs $300-400 at least. Moreover, you still need to get a wave generator, power supply and most importantly a Logic Analyzer if you’re going to write a firmware that interacts with other devices and sensors. A budget of $1K can be easily approached and many students around the world and even engineers could find this a wealth to spend! Yet these tools are things that should be never missed in any bench lab!
To that end, the idea of integrating the most common tools in one device at affordable price is an interesting solution, and that’s what Analog discovery 2 tried to do.
Read more about Analog Discovery 2:
- The Multi-function Instrument “Analog Discovery 2” Review
- ‘Given’ Hardware Behavioral Testing Is Needed ‘Then’ Use Analog Discovery 2 With Behave Python Framework
- Use AD2 to Check FT2232H Outputs
Let’s do a quick review of the features in action, and keep the pros/cons to the end to find if it’s really a Swiss Army Knife as a multipurpose lab bench tool or not.
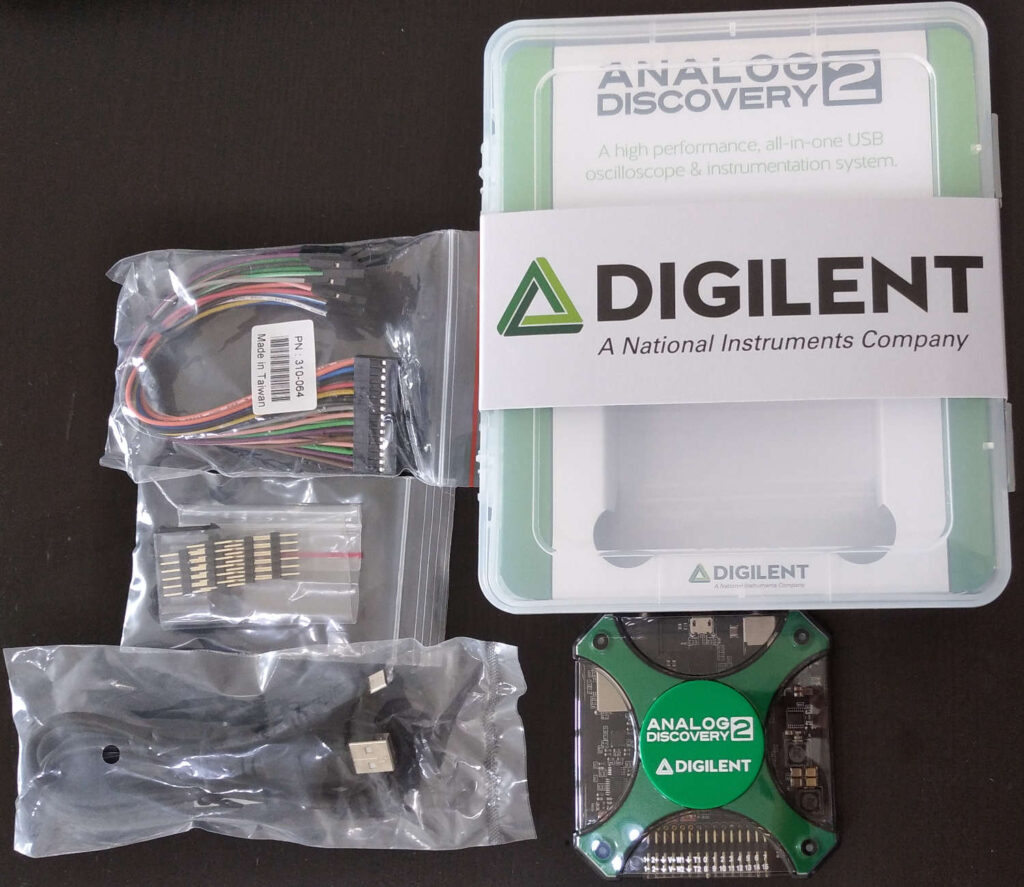

Unboxing Analog Discovery 2 box video:
Software: WaveForms
Analog Discovery 2 uses a PC-based software called Waveforms , which can be found on the Downloads page. WaveForms automatically, and seamlessly, programs the Discovery’s FPGA at start-up. Once programmed, the AD2 communicates with the WaveForms application via a USB 2.0 connection using FT232H USB bridge. The WaveForms software works with the FPGA to control all the functional blocks of the Analog Discovery 2.
As a first impression, Waveforms may not be the most elegant and best UX to have compared to other PC GUI for other AD2-like tools, but more importantly it seems robust enough. To try Analog Discovery out of the box follow the getting started example.
Waveforms includes a demo mode which enables you to explore its features without having connecting Analog Discovery 2. For example, you can select a signal with the signal generator tab and see it on the Scope tab as a demo.

Thankfully, Waveforms is cross-platform and works on Linux- Windows and iOS.
Hardware: Features
‘Everyday Usage’ Features
Oscilloscope
| Channels | 2 |
| Resolution | 14-bit |
| Sample Rate | 30+ MHz (with Discovery BNC adapter) 9 MHz (with included flywires) |
| Sample rate (real time) | 100 MS/s |
| Input Impedance | 1MΩ||24pF |
| Voltage Range | ±25V (±50V diff) Input protected to: ±50V |
| Max Buffer Size | 16384 Samples/channel |
A quick test of any oscilloscope is usually done using the built-in 1kHz square wave test signal, but as Discovery has a built-in wave generator, then It has been used to generate different signals with different shapes and different frequencies and observed in the oscilloscope like the clip below:

You can show spectrum analyzing for the signals within Oscilloscope tab, or you can use the stand-alone ‘spectrum analyzer’ tab with the following features:
| Channels | 2 (Shared with Oscilloscope) |
| Frequency Range | 0Hz to 50MHz |
| Power spectrum algorithms | FFT, CZT |
| Windowing options | rectangular, triangular, hamming, Cosine, and many others |
An important note to drag your attention to is the sampling rate value. AD2 comes basically with a fly-wires unless you order Analog Discovery 2 Pro Bundle. Flywires will limit the sampling rate to 9Mhz. To get the full 30Mhz, you need to use the BNC adapter.


The signals connection is done via a 2 rows connector with 30 contacts. The following pinout demonstrates the function of each pin:

I found the BNC adapter simple, so I decided to DIY one. I ordered BNC connector (Manufacturer Part No: 1-1337543), 2×15 female and male headers ( Manufacturer Part No: 2213R-30G and 2214S-30SG-85 ) and a PCB spacer ( Manufacturer Part No: D01468 ). Beside that I ordered one of the oscilloscope entry-level and cheap probes P6100 (pair for $8). In total, it costs less than $17.

And it did work! Anyway, it’s worth getting the ready-made breakout. It’s available for $20 (probes not included).

Arbitrary Waveform Generator
| Channels | 2 |
| Resolution | 14-bit |
| Sample Rate | 100 MS/s |
| Bandwidth | 12 MHz (with Discovery BNC adapter) 9 MHz (with included flywires) |
| Input Impedance | 1 MΩ |
| Voltage Range | ±5V |
| Max Buffer Size | 16384 Samples/channel |
| Additional Output Port/s | Stereo Audio Output Jack |
AD2 can generate different types of signal with controllable attributes of amplitude, frequency, duty and more. There are many built-in types like the casual (sin, square, triangle, ..etc) signals. Besides that, you can build the wave shape you like by inserting the points value or even entering the mathematical function. In the clip below, both are tested: the built-in type and adding new signals using a mathematical formula.

Moreover, one of the interesting features of AD2 is the Stereo Audio Output using the ordinary audio jack. So you can hear the generated signal! Check the video below:
Finally, Keep in mind the same note mentioned for the oscilloscope, the frequency of the generated signal is affected by the connector type. it is up to 9 MHz with the included flywires or up to 12 MHz using Discovery BNC adapter.
Logic Analyzer
| Channels | 16 |
| Supported Protocols | UART, SPI, I2C, CAN |
| Logic Level | 3.3V/1.2V CMOS, 5V Tolerant |
| Sample Rate | 100 MS/s |
| Max Buffer Size | 16384 Samples/channel |
To test the Logic Analyzer feature, I first tried UART analyzer and I tried different baud rates to check the performance. The test is done using FT232RL USB cable at different baud rates.

This clip shows the usage of this feature step by step.

Another test for Logic Analyzer was using the CAN interface. The analyzer seems to use only one line of the 2 differential data lines (CAN_L and CAN_H). The test is done using PCAN-USB cable @ 125K speed sending 0x41 0x54 0x41 0x44 0x49 0x41 0x54 0x7E message. Another test at a connection speed of 1Mhz showed a successful analysis of the message.

The last test was using showing some SPI messages sniffed from an ESP32 lines to drive one of the SPI TFT screens.

It’s worth mentioning Grabber Test Clips which may be more usable than the flywires in certain cases. Available at the official store for $14.99. However, Can be easily ordered from Aliexpress for lower price.

In the same context, Waveforms provides another powerful tool called ‘Protocol’. In this tab you can sniff or send as a master data over the famous protocols: UART, SPI, I2C and CAN.
Another powerful feature is to write a script to interface with an external device. Here is an official example to talk to an I2C IC like ADXL345. This allows a very quick prototyping and debugging for embedded systems protocols communication.

Programmable Power Supply
| Output Voltage | 0.5V…5V and -0.5V…-5V |
| Maximum Power | 500mW total Maximum Power (USB) 2.1W per channel (External Supply) |
| Maximum Current | 700mA per channel |
Usage of this feature is straight forward, but you need to keep your eye on the limitations of 500mW (that means 100mA max @5V, 166mA @3V, ..etc) when it’s powered from USB and 2.1W (that means 420mA max @5V, 700mA @3V, ..etc) using an external power source.

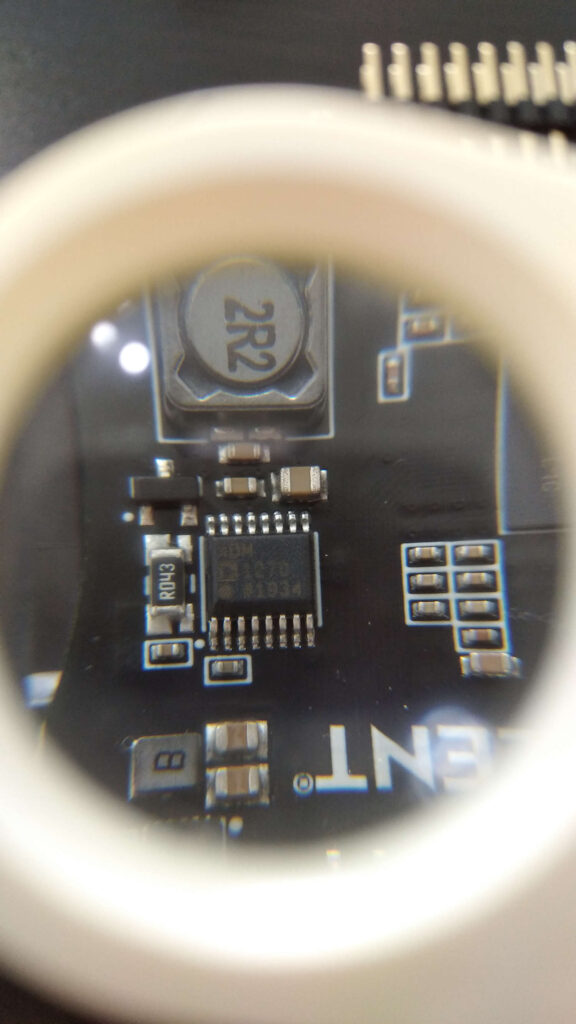
The ADP1612 chip is used as a switching converter in Buck-Boost DC-to-DC topology. Furthermore, ADM1270 is used as a current-limiting controller to provide some power protection while using User Voltage Supplies.
‘Not Everyday Usage’ Features
You may look exactly for one of the following additional features, but they still not the everyday features, I think! And that doesn’t mean they are less important than the other features.
Pattern Generator
| Channels | 16 (Shared with Logic Analyzer) |
| Logic Level | 3.3V CMOS |
| Sample Rate | 100 MS/s |
| Max Buffer Size | 16384 Samples/channel |
A pattern generator is a feature to generate any particular digital signal for debugging purposes. AD2 provides 16 channels. Each channel can individually be programmed or can be used as a group like a bus or truth table. The programmed signal or the pattern is stored in a buffer memory and clocked out at a user-defined sampling rate.
As a simple test for this feature, I defined a ROM Table (Truth Table) for OR gate with 2 inputs and one output. The steps and results are shown in the video below:
This feature is very helpful and can be a powerful tool to do behavioral tests for electronic devices. Out of the mind just now, I could definitely use this feature alongside a test script especially that AD2 provides an SDK and I should be able to integrate into a behavioral testing script written in Python Behave Framework for instance! This could be a subject of a next article.
Data Logger
| Channels | 2 (Shared with Oscilloscope) |
| Supported Measurements | DC, True RMS, AC RMS, Custom |
It is for data collection. It is like the oscilloscope, but used to collect data for a long period of time. For example, you can set it for 1 sample every 1 s for 24 hours, 1 sample every 1 min for 1440 hours, or any other configurations you choose. Later, you can export the collected data in different formats.

Moreover, you can apply some math to your collected data while recording, as shown in the image below:

Impedance Analyzer
| Inputs / Outputs | Shared with Oscilloscope and Waveform Generator |
| Frequency Sweep Range | 100uHz to 25MHz |
| Frequency Steps | 1 to 10000 Plots Impedance, Admittance, Inductance, Capacitance, etc. |
This is another great feature to use when it is important to study the response of your components to a range of applied frequencies. This is a valuable tool especially for high-frequency applications.
Well … the article now is going lengthy and this feature deserves more in-depth exploration in another part, so for now I will show only the example provided in the documentation for this Low-pass filter.

The attenuation of the input signal in the output of Scope 2 is shown in the following graph with the results of analyzing the circuit from 20 Hz to 25 KHz with a 10 kΩ with a 100 samples per frequency point.

You can go beyond the attenuation graph. The things you can analyze are:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Decibel | Measures the input attenuation to the oscilloscope input |
| Phase | Measures the phase adjustment coming into (∠) and from (θ) the system |
| Ohm | Opens the Ohm view of the system including the impedance (|Z|), series resistance (Rs), and series reactance (Xs) over the frequency sweep |
| Siemens | Opens the Siemens view of the system including the admittance (|Y|), parallel conductance (Gp), and parallel susceptance (Bp) over the frequency range |
| Henry | Opens the Henry view showing the series inductance (Ls) and parallel inductance (Lp) of the system over the frequency range |
| Farad | Opens the Farad view to show the series capacitance (Cs) and parallel capacitance (Cp) of the system over the frequency range |
| Dissipation | Shows the dissipation energy ratio of real impedance to the imaginary impedance |
| Quality | Shows the Quality view ratio of stored energy to dissipated energy |
Network Analyzer
| Inputs / Outputs | Shared with Oscilloscope and Waveform Generator |
| Frequency Sweep Range | 1mHz to 10/25MHz |
| Frequency Steps | 1 to 1000 |
It is something I never used before. So please refer to official documentation of this feature, but to give the reader a basic idea of the difference between Network and Impedance Analyzer, I will quote an explanation by one of Digilent staff :
The Network Analyzer is intended to characterize transfer function of amplifiers/filters (C2/C1) mainly in form of magnitude and phase, Bode magnitude/phase, Nichols, Nyquist plots. It has custom scriptable plots that can be used for impedance analysis too. This was added before implementing the IA interface.
The Impedance Analyzer goes further in calculations, it is intended to characterize elements (circuits, components, materials) in complex form like real and imaginary part, resistance and reactance, capacitance and dissipation, inductance and quality. The IA takes in account the scope probe impedance, the value of this can be comparable to the measured element at high impedance and high frequency; open and short compensation; DUT = like R*|C1/C2|- |RC2|- |Open|- |Short|
Static I/O
| Channels | 16 (Shared with Logic Analyzer) |
| Virtual Devices | LEDs, Buttons, Switches, Sliders, Progress Bars, Seven Segment Displays |
You can use 16 channels as a general-purpose I/O pin. Waveforms provides different options to use these 16 channels, i.e. all as input, all as output, inputs progress bar where The digital lines’ binary values are used as bits and highest number digital line is the most significant bit (MSB) or output slider where it configures the eight digital lines according to either the value of the cursor’s position or the value entered in the value field.

Script
If you have a complicated measuring scenario, either you use AD2 with Labview as an available option or you can simply describe the needed steps in a script inside Waveforms and run it. Objects behind the user interface can be accessed from the script code. For example this is a script to send data via SPI using the ‘protocol’ object.

And here is another example of averaging data collected from ‘scope’ object.

Analog Discovery from Inside
We start with the brain of Analog Discovery 2 which is an FPGA chip from Xilinix Spartan 6 Series FPGA, namely XC6SLX16-1L.

As mentioned before, The WaveForms application automatically programs the Discovery’s FPGA at start-up and after being programmed, it communicates with the WaveForms application via a USB 2.0 connection. The USB connection is made using the well known FTDI chips, FT232H.

The block diagram of Discovery electronics design is shown below:
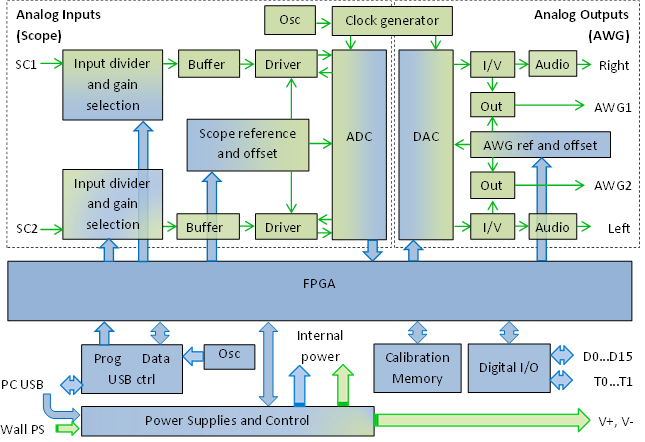
Another chip to show is for the wave generator functionality, the DAC chip. Discovery uses a dual-channel 14-Bit Low Power Digital-to-Analog Converters chip from Analog Devices called AD9717.

ADC is the backbone in any Oscilloscope, AD2 uses a 14 -Bit, 125 MSPS/105 MSPS, 1.8 V Dual Analog-to-Digital Converter from Analog Devices called AD9648.

The last chip to highlight for now is ADN1270 which is used to provide some power protection while using User Voltage Supplies.
However, a high-resolution shot of top and bottom views of Discovery PCB is helpful to look at.


Finally, For whom are interested to see more low level and Analog details, you can refer to the official reference manual page.
Conclusion
At the time of writing this review, we are in the middle of coronavirus COVID-19 pandemic and most companies are switching to a remote working environment and such tools should be a great deal.
As far as my test went with this multi-purpose tool, it seems it really deserves to be called a Swiss-Army knife tool. The Software tool showed a robust performance and during the review I encountered only 2 crashes, and that was at the beginning and maybe because of miss-using something. Yet the WaveForms user experience needs enhancements to make it more friendly, but once you get used to the features, it won’t be a big deal. However, I found a nice user experience for a similar Web-based app from also Digilent called WaveForms Live designed for OpenScope MZ.

Moreover, I found the need to get an adapter to get the full frequency performance a little annoying. Especially that, this will add $20 for the adapter and yet another $20 for the probes. Unless you order Analog Discovery 2 Pro Bundle for $300 from the first place to save $20 a head.
It is nice if the next generation of Analog discovery can integrate the BNC connectors inside the case or at least 2 shared ones for oscilloscope/generator channels. Another comment on the web I saw about the BNC breakout and expressed a concern I had is: “I want some protection for the BNC breakout, which I feel is too exposed for a messy workbench (like mine)”.
Finally, if you really like the Waveforms, but you still find Analog Discovery costly, then maybe OpenScope MZ form also Digilent with less capabilities and less price ($150), but same functions is something you need to consider. However, To be more sure about your choice, it’s advised to read Knowm’s quick compassion made between different USB instruments in the market with AD2.
What’s Next?
- Take a look at the full list of official tutorials for almost all features AD2 has.
- Read about advanced usage of AD2 .i.e: Measuring current, cross-triggering.
- Explore the usage of Analog Discovery 2 with Labview.
- Learn how to develop custom software solutions using WaveForms SDK.
What is your opinion?
What do you think about AD2? Do you suggest other multi-function instruments like ADALM2000 from Analog Devices for example? Please share your thoughts in a comment.
Read more about Analog Discovery 2:
- The Multi-function Instrument “Analog Discovery 2” Review
- ‘Given’ Hardware Behavioral Testing Is Needed ‘Then’ Use Analog Discovery 2 With Behave Python Framework
- Use AD2 to Check FT2232H Outputs

